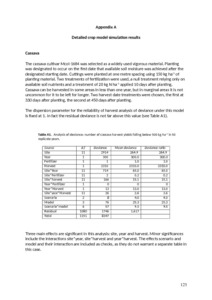
Grassland degradation reduces the carbon sequestration capacity of the vegetation and enhances the soil carbon and nitrogen loss
Grassland degradation not only results in soil degradation and severe decreases in land productivity, but also can promote the emission of soil carbon and nitrogen compounds as greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The primary objective of this study was to characterize the impact of grassland degradation on carbon and nitrogen budgets in Inner Mongolia, China.